The Agency Theory Can Best Be Described as
Using this conceptualization agency includes two areas. In an agency relationship two parties exist the agent and principal whereby the former acts and takes decisions on behalf of the latter.
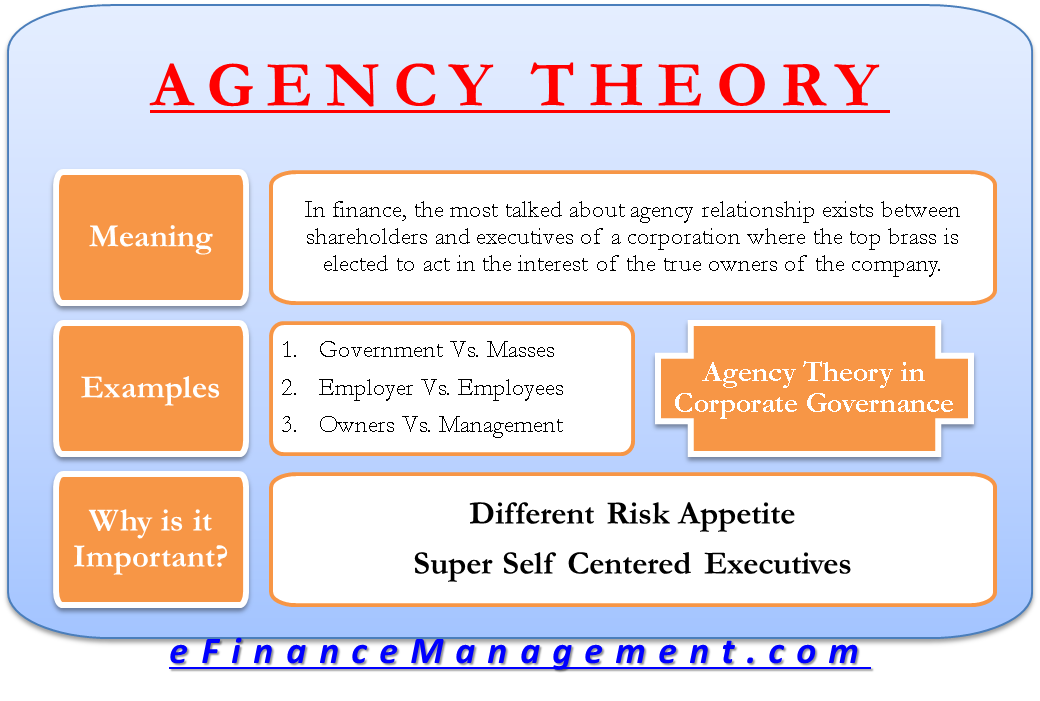
Agency Theory In Corporate Governance Meaning Example Importance
This work is framed by agency theory using OMeara Campbell Teroskys 2011 definition of agency as an attribute of an academic member that is evidenced by hisher assuming strategic perspectives andor taking strategic actions toward goals that matter.

. Being based only on observations. The problem here is that the prin-. Absolutely constrained beyond a certain boundary absolutely free or devolving upon the individual within it.
An Explanation - Seven Pillars Institute Agency Theory Agency Theory explains how to best organize relationships in which one party determines the work while another party does the work. It also describes the conflict of interest or relationship that arises between agents and principals. Agency theory is an approach that explains a situation whereby an agent acts on behalf of a principal to contribute to the progress of the principals goals.
Agency theory is a management and economic theory that attempts to explain relationships and self-interest in business organisations. It has application to accounting industrial organization and labor economics and it has become the basis of the economic model of compensation. This is a common way ever since the Enlightenment to describe the agency of individuals.
This most importantly means the conflicts between. Agency theory is a management and economic theory that attempts to explain relationships and self-interest in business organisations. Description explanation or prediction of accounting practice based on observations andor logical reasoning.
At the heart of agency theory is the idea that civil-military relations is essentially a form of strategic interaction between civilian masters principals and their military servants agents. Agency theory examines the relationship between the agents and principals in the business. This theory was developed by Stanley Milgram the American psychologist who carried out the famous Obedience Studies.
The history of agency problem dates. It describes the relationship between principalsagents and delegation of control. This principal-agent relationship exists between employers and employees lawyers and clients or buyers and suppliers.
Agency theory is concerned with resolving two problems that can occur in agency relation- ships. Being irrelevant to the development of new practice and procedures. Agency theory is concerned with resolving problems that arise in agency relationships.
Agency theory describes the problems that occur when one party represents another in business but holds different views on key business issues or different interests from the principal. Agency refers to the thoughts and actions taken by people that express their individual power. Agency Theory The study of the relationship between an agent such as a broker and a principal such as a client.
The bounded circle of agency. Agency exists within tight constraints but is free within those constraints. Agency theory seeks to explain the relationship in order to recommend the appropriate incentives for both parties to behave the same way or more specifically for the agent to have the incentive to follow the principals direction.
In this relationship the principal hires an agent to do the work or to perform a task the principal is unable or unwilling to do. The first is the agency problem that arises when a the desires or goals of the principal and agent conflict and b it is difficult or expensive for the principal to verify what the agent is ac- tually doing. One boss or Principal and one worker or Agent.
AGENCY THEORY Agency theory pertains to the relationship between two parties. Agency theory is one of the most important developments in microeconomics in the past 20 years. Milgram developed his ideas as a response to Nazi war crimes especially the trial of.
Agency studies incentives risk and selection of employees. A self-interested b boundedly rational and c different from principals in their goals and risk-taking preferencesthat a problem occurs when one party a principal employs another an agent to make decisions and act in their stead. Agency theory arguesusing fundamental assumptions that agents are.
Agency Theory This note considers the simplest possible organization. Agency theory is the branch of financial economics that looks at conflicts of interest between people with different interests in the same assets. A set of facts specific in nature against which accounting practice can be evaluated c.
An agency relationship is described as a situation in which one party the principal delegates work to another party the agent. The first is the principal or principals and the second the agent or agents who are engaged as employees or independent contractors. Considered a subunit of the theory of contracts agency theory deals with the determination of the general structure of such contractual relationships and factors.
MILGRAM 1973AGENCY THEORY EXPLAINS BLIND OBEDIENCE. Agency and Career Coherence. In an agency business a principal hires an agent to represent them or work for them.
In that strategic interaction civilians choose methods by which to monitor the military. An agency relationship in which the agent represents two principals simultaneously without their knowledge or permission universal agent a person empowered to do anything the principal could do personally the authority to act on the behalf of the principal is virtually unlimited. Shareholders and managers of companies.
Agency theory revolves around the issue of the agency problem and its solution Jensen. One of the earliest applications of this Principal-Agent model was to sharecropping where the landowner was the Principal and the tenant.

Principal Agent Theory An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
/BernardMadoff-2a08894ef4db4d0fbabc93b6d91afeae.jpg)
Comments
Post a Comment